Solar power has been declared the most affordable form of electricity by the International Energy Agency’s World Energy Outlook 2020. Solar power is a type of renewable energy that uses energy from the sun to generate electricity. This renewable energy source is also easily accessible and environmentally friendly, making it an attractive option for homeowners. However, before making the switch, it’s essential to understand the different types of solar power systems available.
The two most common options are the grid-tied solar energy system and the hybrid solar energy system. Grid-tied solar systems are connected to the main power grid, and any excess power generated by the solar panels can be sold back to the power company. On the other hand, Hybrid systems combine the features of both grid-tied and off-grid systems, and they are becoming increasingly popular as they offer the best of both worlds.
Both systems rely on solar PV panels to generate electricity, which is converted into usable power with the help of an inverter. Depending on the type of system used, the solar energy produced can be consumed, stored, or sold back to the grid. To gain a deeper understanding of these systems, the following provides a detailed overview of both options. Reviewing this information lets you determine which solar energy solution best suits your needs and preferences.
Grid-Tied Solar System
The most commonly used solar systems for homes and businesses are on-grid or grid-tied solar power systems. These systems do not require batteries and instead use solar inverters or micro-inverters to connect to the public electricity grid. Any surplus solar power generated is typically exported to the grid, and you may receive payment through a feed-in-tariff (FiT) or energy credits for the exported energy.
A grid-tied solar system, also called utility-interactive, grid intertie, or grid back feeding, is a solar power concept linked to the utility’s power grid. By eliminating the need for batteries and other equipment for energy storage, grid-tied solar system designs are generally less expensive and easier to install, resulting in increased efficiency rates and net metering, which saves you money on solar panel costs.
Net metering is a billing arrangement that allows homeowners with grid-tied solar systems to receive credits for excess electricity generated by their solar panels. This means homeowners can sell the excess electricity to the utility company and receive credits on their electricity bill, reducing their overall cost.
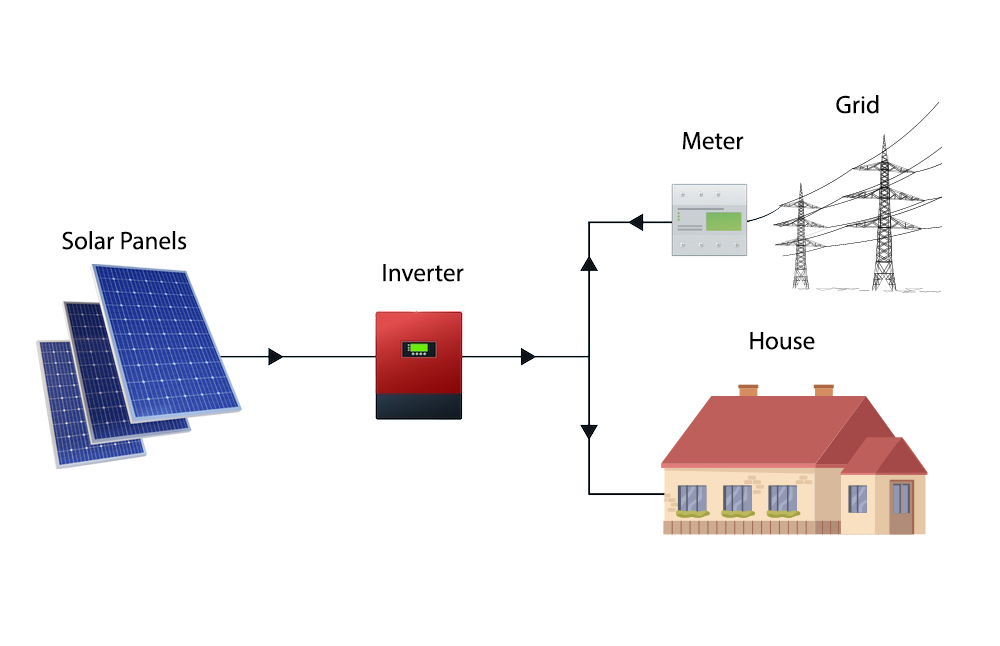
Working of Grid-Tied Solar System
Designing a grid-tied solar system involves connecting the solar panels to an inverter, which converts the DC power produced by the panels into AC power that can be fed into the power grid. This system does not require batteries to store excess energy, as any surplus electricity generated by the solar panels can be automatically sent back into the grid for use by others. The system relies on net metering, which allows homeowners to receive credit for the excess electricity they generate and feed into the grid.
Any excess energy produced by the complete grid-tied solar systems is fed back into the connected power grid. This system allows for net metering, enabling users to export surplus energy to the public grid beyond their household requirements. The users are compensated for this energy through a feed-in-tariff (FIT) mechanism that follows net metering policies that may differ in various regions.
Components of Grid-Tied Solar Energy Solution
The components relied upon in typical solar systems that are connected to the electrical grid include:
Grid-Tied Inverter (GTI)
Grid-tied inverters are crucial in controlling the voltage and current supplied by your solar panels. They convert the direct current (DC) solar panels generated into alternating current (AC), compatible with most electrical appliances.
Moreover, these inverters ensure synchronization of phase and frequency of the current with the utility grid frequency, which typically operates at 60Hz. Additionally, the inverter’s output voltage is set slightly higher than the grid voltage to allow any excess electricity generated to flow back into the grid.
Micro-Inverters
Micro-inverters are individual inverters installed at the back of each solar panel, in contrast to a central inverter that typically handles the entire solar array. Although micro-inverters are more expensive than central inverters, they provide higher efficiency rates. If an installation is likely to experience shading issues, it is strongly advised to use micro-inverters.
Net Meter
Net metering is a billing system that compensates owners of solar energy systems for the electricity they generate and contributes to the grid. This system utilizes a two-way meter, or net meter, that measures power flow in both directions, from the grid to your home and from home to the grid. It is imperative to consult with your local utility company to explore available net metering options.
Advantages of Grid-Tied Solar Energy Solution
The following advantages of grid-tied systems make it possible to recover the investment in the expensive plan.
Save More Money
Net metering allows you to sell excess electricity generated by your solar panels back to the utility grid, enabling you to offset your electricity usage charges up to 100%. This incentivizes residential solar power systems, making them financially feasible and the cheapest grid-tied solar system.
Easy Installation
Compared to other solar systems, grid-tied solar systems is cheaper and easier to install, as they do not require a battery. Additionally, they have lower maintenance requirements.
Use the Utility Grid as a Virtual Battery
The utility grid functions as a battery without needing maintenance or replacements and with higher efficiency rates than traditional lead-acid batteries. By being a grid-tied solar electric system, you have access to backup power from the utility grid and help reduce the utility company’s peak load, increasing the efficiency of the electrical system overall.
Disadvantages of Grid-Tied Solar Energy Solution
Here are some disadvantages of the grid-tied solar system:
Heavily Relies on the Grid
The grid-tied solar system cannot operate independently if the grid experiences any malfunctions. If the on-grid solar inverters continue to supply electricity to the faulty grid, it may pose a significant risk to residents in the surrounding area.
Not Include Battery Backups
The grid-tied solar system does not include any battery backups to store excess solar energy generated during the day for future use. Consequently, it cannot generate power during periods when there is no available solar energy input.
Hybrid Solar System
A hybrid solar system design is similar to a grid-tied system in producing solar energy, but it offers the additional advantage of grid independence. It operates 24/7, regardless of the grid’s availability, storing excess energy for nighttime use. This energy backup allows a hybrid solar system power generation to function seamlessly during power outages or blackouts. Also, adequate energy storage can help reduce peak-time usage, which is usually charged more than off-peak consumption. Any new solar generation can be exported back to the grid. As a result, hybrid solar systems in Pakistan can provide more significant savings and faster returns on investment.
How a Hybrid Solar System Functions
A hybrid system combines off-grid and on-grid solar systems, including battery backup and a connection to the grid. Unlike an on-grid system, a hybrid PV system is not entirely reliant on the grid for its operation but uses its battery backup instead to provide energy when needed.
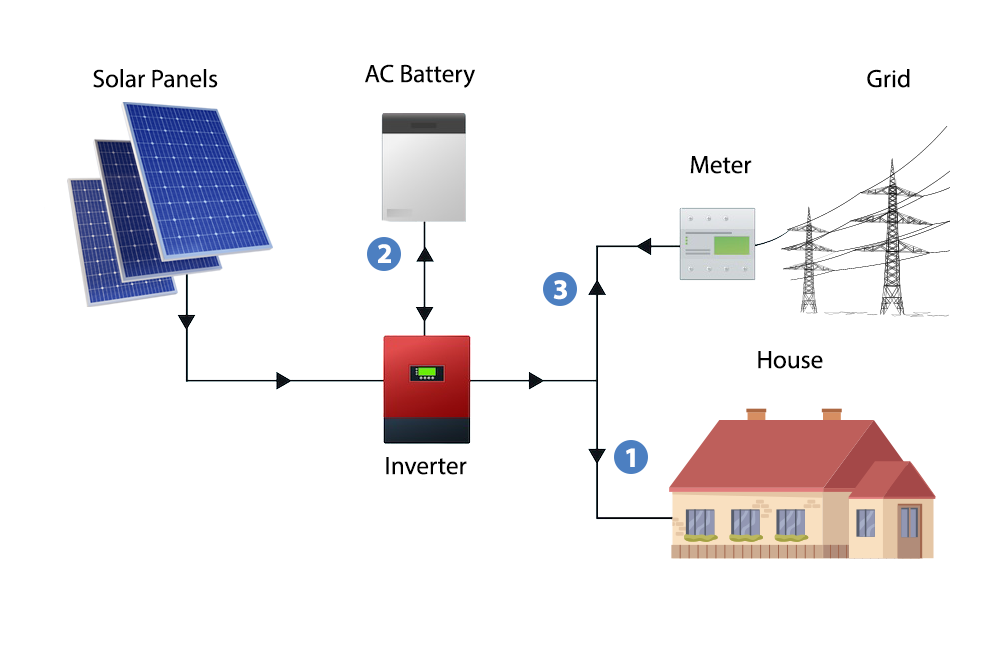
Components of Hybrid Solar Energy Solution
The essential components of a solar system connected to form the hybrid system are as follows:
Charge Controller
A hybrid solar charge controller is the component of a hybrid system that regulates the voltage and current from the solar panels to prevent overcharging of batteries. It ensures maximum power output and improves the lifespan of the batteries by controlling the amount of electricity that flows into them.
Battery Bank
An essential part of a hybrid system is using a hybrid battery for solar energy storage in case excess solar energy is generated, which can be used at night or when there is less sunlight. The size of the battery bank depends on the amount of energy needed to power the home, and it is crucial to select the right type and capacity of batteries to ensure optimal performance.
Direct Current Disconnect
A DC disconnect is an additional safety device that disconnects the solar panels from the best hybrid solar inverter and battery bank. It is essential to ensure that no electricity flows through the system during maintenance or repair, preventing electric shock or damage to equipment.
Battery-Based Grid-Tied Inverter
A battery-based grid-tied inverter is used to convert the DC power from the solar panels and battery bank into AC power that can be used by appliances in the home or sent back to the grid. This type of inverter ensures that power is available even during a blackout or power outage, and excess energy can be sold back to the grid, reducing electricity bills.
Power Meter
A power meter measures the electricity generated by the solar panels, consumed by the home, or sent back to the grid. This information is crucial for monitoring the system’s performance, optimizing energy consumption, and tracking savings. A power meter can be installed on the inverter or as a separate device, providing real-time data to the homeowner or installer.
Advantages of Hybrid Solar Energy Solution
The following advantages of a hybrid solar inverter make it a worthwhile investment that can pay off in the long run.
Uninterrupted Supply
A hybrid solar energy system provides an uninterrupted power supply, even during blackouts and load shedding. The unused solar energy generated during the day is stored in batteries for later use, ensuring the availability of a backup source of power. Mainly it is beneficial in areas that experience frequent power outages or unreliable grid connections.
24/7 Power
Due to their battery backup, hybrid solar systems can power homes 24/7, even during grid outages. This means homeowners can rely on their solar system to provide electricity day and night, reducing their dependence on the grid. With a hybrid system, homeowners can be confident they will always have access to a reliable power source, regardless of the time of day or weather conditions.
Policy Independence
Hybrid solar inverters depend less on changing net-metering policies and offer high reliability due to their grid and battery backup. This means that homeowners can continue to generate and store their electricity, even if net-metering policies change or the grid connection becomes unreliable. Hybrid systems also offer a high degree of independence from utility companies, allowing homeowners to take control of their energy generation and consumption.
Net-Metering Savings
Surplus solar energy is exported to the grid for net metering, leading to significant savings on electricity bills and reducing dependence on the grid. With a hybrid solar inverter in Pakistan, homeowners can generate electricity and sell surplus energy back to the grid, reducing their reliance on traditional electricity providers. This can lead to significant savings on electricity bills and a reduced carbon footprint.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Solar Energy Solution
Here are some of the disadvantages of the hybrid system:
High-Cost
Hybrid PV systems can be costly due to the combined expense of the hybrid inverter and solar battery.
Maintenance Required
Hybrid solar energy solutions generally require more maintenance than grid-tied systems due to the additional components such as batteries and inverters.
Short Battery Life
The battery life of hybrid solar power systems is relatively shorter, lasting 7 to 14 years.
Conclusion
The working methodology of grid-tied and hybrid solar systems is similar. They convert solar energy into DC power and then use inverters to convert it into AC power for running home appliances. The key difference lies in the storage of excess energy. Hybrid systems store it in batteries for later use, while on-grid systems export it to the grid and receive credits. Hybrid systems offer excellent reliability, while grid-tied plans are more budget-friendly. Therefore, after understanding the comprehensive explanation of both systems, one can choose the solar system that best suits their needs.
However, the best grid-tied solar systems cannot generate power during blackouts due to safety concerns. If a damaged grid is still receiving electricity from a solar inverter, it could endanger the people repairing the network. In contrast, hybrid solar systems with battery storage can automatically isolate from the grid and continue to supply power during blackouts. Both hybrid and grid-tied solar energy systems have unique benefits, and the choice between them ultimately depends on the specific needs and goals of the individuals.
It is essential to carefully consider the factors involved in making this decision, such as the availability of sunlight, the cost of installation and maintenance, and the environmental impact. Ultimately, the urgent need to transition to renewable energy means that the decision to adopt a solar energy system should be completed on time. By taking action now, we can contribute to a more sustainable and secure future for ourselves and future generations.
FAQs
A grid-tied solar system is a solar energy system connected to the utility grid. It is designed to supply electricity to your home when the sun is shining and excess electricity is generated and to draw power from the grid when the sun is not shining.
Grid-tied solar systems convert solar energy into electricity, which is used to power your home’s electrical system. Any excess energy that is not used is sent back to the grid, and you are credited for this energy on your electric bill.
No, a grid-tied solar system requires a connection to the utility grid, so it cannot be installed in a remote location without access to the grid.
A hybrid solar system combines a grid-tied solar system and an off-grid one. It is designed to provide electricity to your home from solar energy when available and switch to battery backup power when there is no sun or during power outages.
A hybrid solar system uses solar panels to generate electricity during the day, which is used to power your home and charge the batteries. The batteries store excess energy, which can be used at night or during power outages.
Yes, a hybrid solar system can be installed in any location with access to sunlight. Still, the installation cost may vary depending on the site and the homeowner’s needs.




Add a Comment