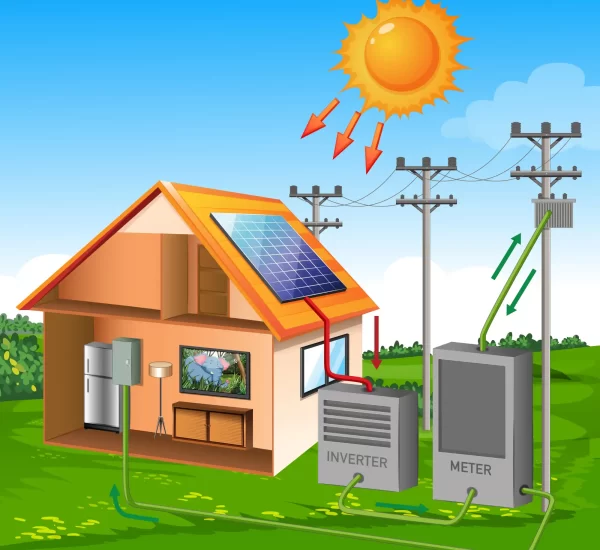
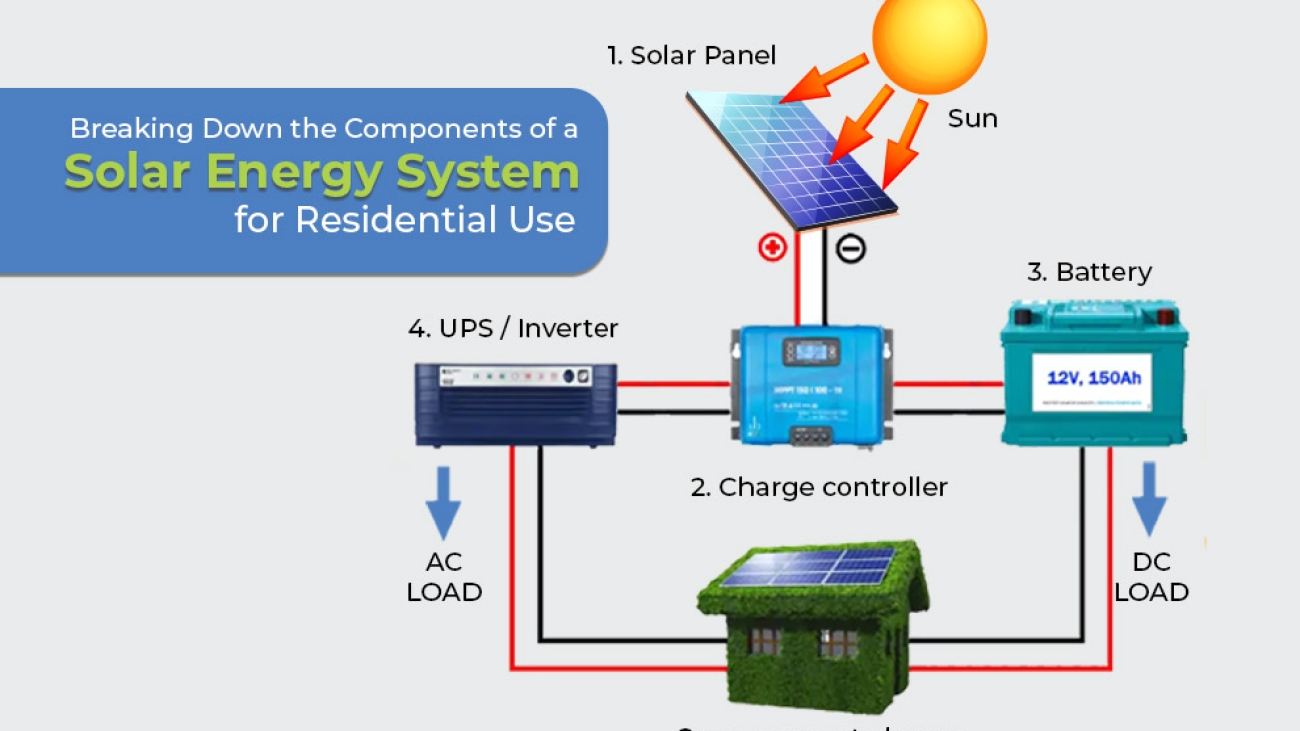
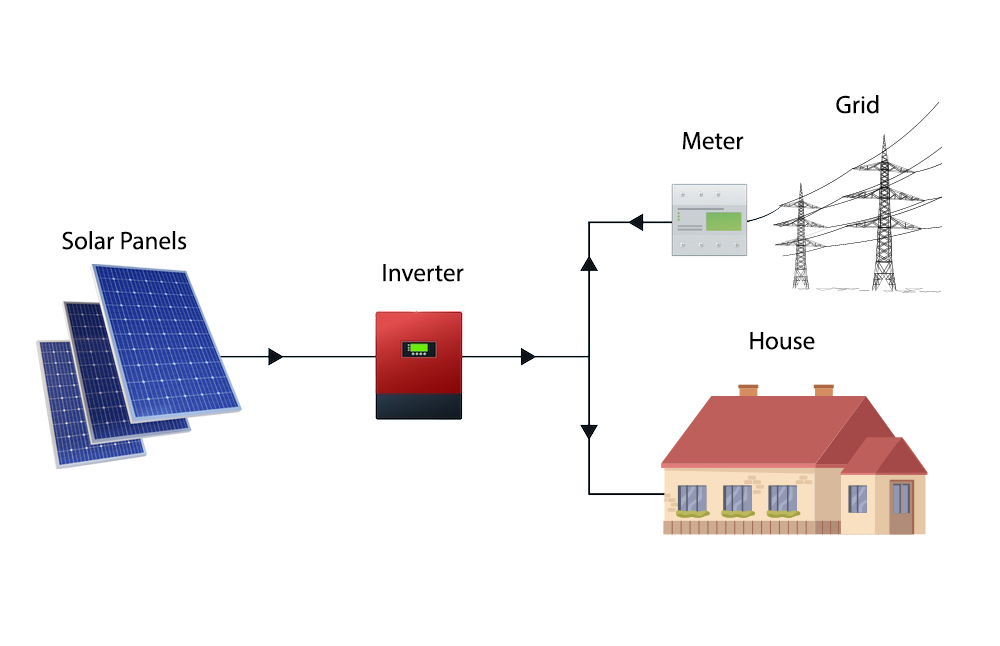
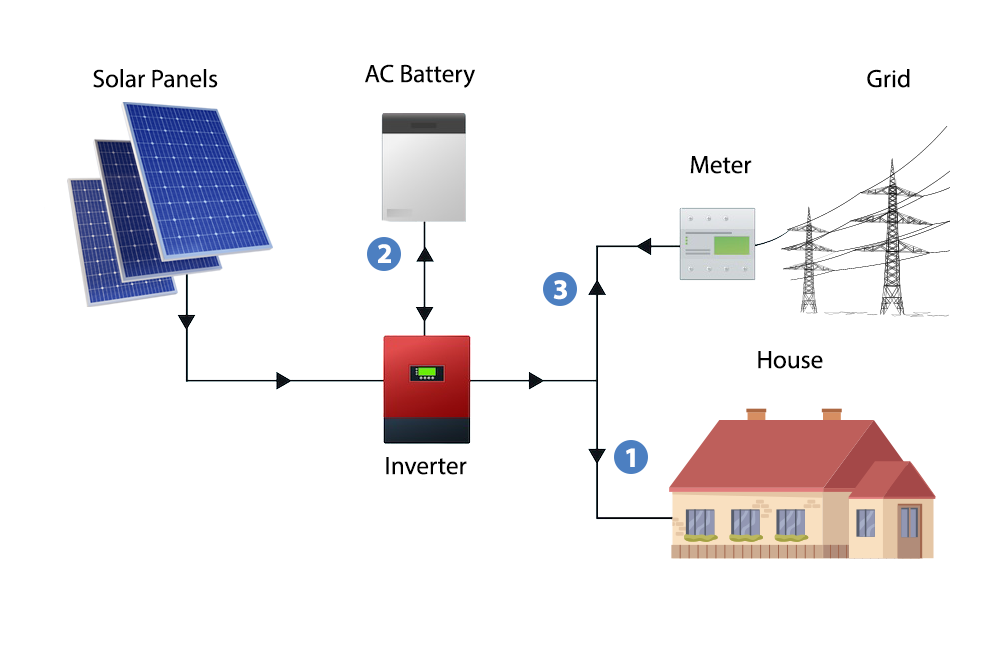
What image comes to mind first when you think of solar energy? We’re assuming that you’re considering some of these!

As we are all aware, solar energy systems consist of more than just panels. There are many components of the solar energy system, each includes with various brand options which can greatly impact the system’s functionality and offer extraordinary features. This can make the solar installation process very intimidating for many people, but don’t worry – we’re here to help!
This article aims to assist those who are new to the field in understanding the investment they are considering for their homes and businesses. We also aim to help those who already have systems. We better understand all the components and how they work together to power home or business. To fully comprehend the anatomy of a solar energy system, it’s crucial to have a thorough understanding of the system as a whole, including its various components.
Solar Energy System
Solar energy systems are renewable energy generation systems that capture solar energy using photovoltaic technology, converting it into usable electricity. These systems come in various sizes to cater to the energy needs of residential, commercial, or utility-scale properties and have diverse applications. They include traditional rooftop or ground-mounted systems for powering buildings, as well as unconventional methods that can power other objects such as space satellites, handheld calculators, or vehicles.
A standard solar power system for residential or commercial use comprises essential components of a solar energy system, including solar panels, inverters, DC/AC disconnects, meters, wiring, racking, and mounting. These systems are usually grid-tied, but some require additional components beyond the core set, such as charge controllers, batteries, and other balance-of-system items, for off-grid use.
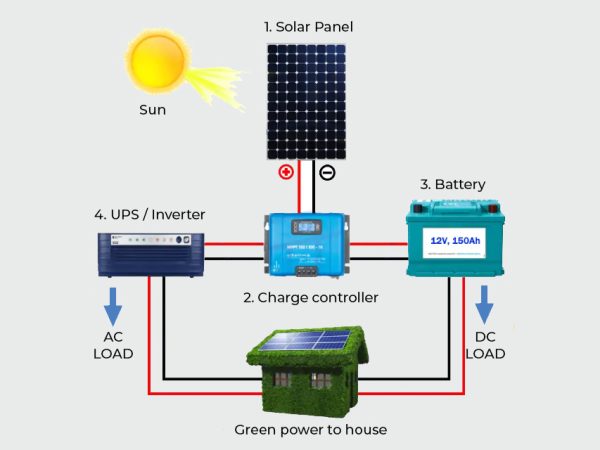
Solar Panels
The solar panel or PV module is the most widely recognized component of a photovoltaic array. It comprises solar cells, framing, and glass. These panels collect and harness photovoltaic energy from the sun and generate ‘direct current’ (DC) power, which is directed to an inverter or converter component. In some cases, this component may be a charge controller.
The DC power produced by a solar module is a type of electric current that flows in a constant direction. However, this form of energy is generally not suitable for powering standard electric devices. It must be transformed into ‘alternating current’ (AC) power before operating electrical appliances within a home or building.
Types of Solar Panels
There are two widely recognized types of solar cells used in solar panels: Polycrystalline and Monocrystalline. The difference between the two types is based on how silicon crystals are harvested, developed, and formed in the ingots or wafers, which gives them their distinct appearance and color. Despite their differences, both types of PV cells are known for their effectiveness in producing solar electricity. Thin-film solar cells, which are less commonly used than monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels, represent a third type of solar panel in Pakistan.
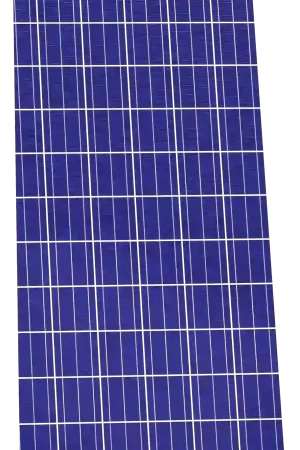
Polycrystalline Silicon Panels
These panels are made of multiple silicon crystals combined, making them an economical option. They are commonly used as grid-tied solar panel components. However, they are less efficient than monocrystalline panels.
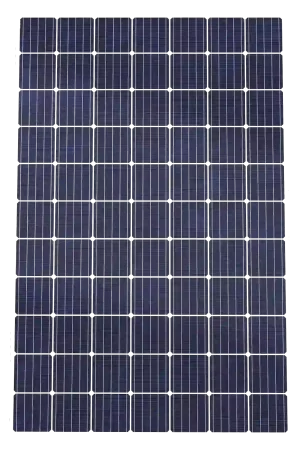
Monocrystalline Silicon Panels
These panels are made of a single crystal, making them the most efficient type of solar panel and the industry standard. However, they are also the most expensive option available.
Thin-film Solar Cells
These cells are made using amorphous silicon and are the most flexible type of solar panel. They may be a suitable choice if you need to install panels on a curved surface or for off-grid setups such as RV solar panels. However, these panels are generally the least efficient of the three types mentioned above.
Solar Inverter
Inverters, also known as converters, play a crucial role in a solar energy system by converting the DC power generated by solar panels into AC power that can be used for standard electrical devices. The solar inverter can be located after a charge controller and battery bank in off-grid energy systems. The best solar inverters in Pakistan come in various sizes and use different technologies to convert DC to AC power efficiently.
Types of Inverters
There are four common types of inverters: String inverters, string inverters with PV optimizers, microinverters, and battery-based inverters, each with unique mechanical and technical characteristics.

String Inverters
These are a type of central unit with inputs for groups of solar panels known as strings. In a string inverter system, the solar panels are connected in series, with the last panel in the chain plugged into an input. For instance, an 8 kW kit may have two strings of 10 panels each, totalling 20. String inverters are the most affordable option when building a solar system in full sunlight. However, shading can cause problems for string inverters. When one panel in a string is shaded, its output decreases, and the output of the rest of the series drops to match the reduced production of the shaded panel. If the building site is obstructed by trees, chimneys, or other objects, a string inverter alone will not be sufficient to obtain the maximum output from the solar array. In such situations, it is advisable to include PV optimizers to minimize the impact of shading.
String Inverters
A PV optimizer is a device that can be attached to the back of each solar panel in an array. It functions by separating the output of each panel, which enables it to generate power and communicate its performance to the monitoring system individually, without any influence from other panels in the array. This means that if any panel is obstructed by shade or any other issue, only that particular panel's output will be affected. The other panels in the array will continue to function at their full potential without any reduction in performance. Moreover, PV optimizers provide the advantage of individual panel-level monitoring, allowing you to track the performance of each panel in your monitoring portal. If any panel is underperforming, you can quickly identify it and take the necessary steps, such as cleaning or replacing it, to rectify the problem. In contrast, string inverter systems only monitor the system's overall performance, and identifying the issue with individual panels can be time-consuming and challenging.

Microinverters
Microinverters are devices that are attached to the back of each solar panel in an array to optimize the system's output and enable individual panel-level monitoring similar to PV optimizers. However, unlike optimizers, microinverters don’t need a centralized string inverter unit to connect the system. Instead, the microinverter unit itself handles the inverting capabilities. This means that each panel-microinverter combination acts as a self-contained solar power system, making the design of microinverter systems more flexible, modular, and expandable than string inverter systems. For instance, you can start with a small system and expand it later without retrofitting or re-installation. Additionally, you can place panels on different roof facings without stringing panels together, which is beneficial for oddly-shaped roofs. You can also repair or replace individual panels or microinverter units without disrupting the system. While microinverters may be initially more expensive than string inverters, they offer better long-term value due to their extended warranty period. String inverters usually have 5-15 years warranties and often require replacement in the middle of your system's lifespan. On the other hand, Enphase's IQ7 series microinverters come with a 25-year warranty, which is equivalent to the length of most solar panel warranties.
Battery-Based Inverters
Grid-tie inverters like the SMA Sunny Boy are not designed to charge batteries. If you plan to incorporate energy storage into your solar system, you should consider using an inverter that can facilitate battery charging. These types of inverters are known as "hybrid" or "storage-ready" inverters. The Enphase Ensemble package is an excellent choice for those looking to add storage to a microinverter system. It seamlessly combines Enphase's microinverters, batteries, and monitoring into one system, making it simple to install and compatible as all components are enphase native. Another option is the Sol-Ark all-in-one hybrid solar inverter, which integrates inverting, charging, and monitoring into a single unit. This reduces the number of components needed for installation, making it even easier to set up. However, the downside is that it is less flexible and expandable than Enphase's modular system.
Monitoring
Monitoring equipment is typically linked to an inverter manufacturer and transmits system energy data analytics to a product console or web-connected device through proprietary software. These components are incorporated into an inverter or connected to another element of a photovoltaic array.
Monitoring technology can provide information on various aspects of solar panel performance, including real-time data, immediate fault detection, troubleshooting, and energy yield data over a specified period.
A comprehensive monitoring system can help system operators better understand their solar energy system’s operation in real-time or over its lifespan, enabling them to take measures to increase yields, productivity, maintenance, and other variables.
Racks and Mounts
Racking and mounting components are critical for connecting a PV array to the ground or a roof and typically comprise various products that make up a complete racking system. These systems often comprise a combination of rails, flashings, clamps, mounting brackets, wire clips, splice kits, braces, end caps, attachments, tilt legs, and other components. To create a stable foundation, concrete and steel piping may also be necessary for ground mount systems.
Types of Racking
Racking and mounting are pivotal components of any solar energy system, whether installed on a rooftop or the ground. A reliable and sturdy structure is necessary to ensure the system’s integrity and longevity of operation.
Roof Mount Racking
To install solar panels on your roof, you must use your home’s rafters to support the solar array’s weight. This involves locating and marking your roof rafters, which can be done using a stud finder or by measuring their position inside your attic.
Roof mount systems are the standard choice for most residential solar installations because they are cost-effective and save valuable space, making them ideal for homeowners with limited yard space. A roof mount is typically the most cost-effective option if you have a suitable South, West, or East-facing roof with sufficient space to accommodate your array.
Ground Mount Racking
A ground mount is a freestanding structure composed of metal pipes that are firmly anchored in concrete footings in the ground. Compared to a roof mount, a ground mount system requires more time and money to install as it involves constructing a new structure to support the solar array.
One of the advantages of ground mounts is that they offer more flexibility in terms of panel orientation. You can position the panels directly toward the Equator and adjust the angle to maximize the system’s output. In contrast, with roof mounts, you are limited to the orientation and tilt of your rooftop.
Ground mounts are also more accessible for routine maintenance and cleaning. With a ground mount system, you won’t need to climb onto your roof to clean the dust off the solar panels.These are particularly suitable for commercial and rural properties with ample space to build an array that fully utilizes the capacity of their solar panels.
Pole Mounts
Pole mounts are a type of ground mount that use a tall pole to elevate solar panels high off the ground. They are particularly useful in specific scenarios:
They are instrumental in the following specific scenarios:
In snowy climates, pole mounts can tilt panels at a steeper angle, allowing the weight of snow to slide off the face of the panels. Additionally, they can be raised higher in the air to provide clearance over snowbanks that accumulate in the winter months.
On hillside installations, steep slopes can present challenges for standard ground mounts, which require several distributed concrete footings to anchor the support in place. Digging deep enough trenches to pour the concrete and level off the mount on a steep slope can be difficult. However, pole mounts only require one anchor point, making installing them on a steep hillside much simpler.
Ballasted Racking
A ballasted racking solution is a type of mounting system that consists of a container with a frame that enables you to mount your solar panels. The container is filled with ballast, a dense material like gravel or dirt, which provides sufficient weight to hold the system in position.
Ballasted mounting systems do not require holes to be dug and concrete to be poured to anchor the mount into the ground, as they depend on counterweights to keep the system secure. As a result, these systems are less expensive, less complicated, and faster to install.
Balance of system
The Balance of System (BoS) components are designed to integrate and connect various electrical products in a PV system, facilitating power control and distribution. A typical BoS kit includes DC/AC Disconnects, Junction Boxes, Combiner Boxes, Circuit Breakers, Fuses, Load Centers, Rapid Shutdowns, Surge Devices, and other components that may vary depending on the application.
The configuration of BoS components varies from system to system, depending on the required power control and distribution options. These components play a crucial role in safeguarding and maintaining the integrity of the system and facilitating emergency maintenance in case of any potential issues, such as fire or other hazards. Power control is an important aspect of any electrical generating system.
DC Disconnect Switch
DC disconnects are devices that can either complete or break the flow of DC electricity. In a solar PV system, a DC disconnect is placed between the solar panels and the power inverter, allowing for easy interruption of solar power if needed, such as during maintenance or emergencies. Additionally, DC isolator switches are installed in PV systems to allow for the manual disconnection of solar panels during installation, maintenance, and repair.
Junction Boxes
The junction box is a crucial component that links the solar panel to the charge controller, serving as an interface between the two. It is an essential part of a solar energy system and requires a comprehensive design that incorporates electrical and mechanical engineering and materials science elements. The junction box provides users with a combination connection scheme for solar panels, and it plays a critical role in enabling the system to function efficiently.
Circuit Breaker
Circuit breakers are a critical component in solar systems, serving as safety devices that protect the system from overloads, short circuits, and other electrical faults. They act as a barrier between the direct current (DC) generated by the solar panels and the alternating current (AC) used by household appliances and the electrical grid.
In the event of an electrical problem, the circuit breaker automatically interrupts the flow of electricity, preventing damage to the system and reducing the risk of fire or other hazards. Circuit breakers also make it easier to perform maintenance on the system by allowing specific sections to be turned off without affecting the entire system.
DC Fuse Holder
In the event of excess current flowing through the circuit, the DC fuse interrupts the flow. Unlike in AC circuits, extinguishing the arc in the DC circuits is not as simple. DC fuses protect battery modules and packs and provide adequate clearance of DC fault currents.
Load Centre
Solar load centers are essential for solar power systems, as they are designed to meet the unique needs of photovoltaic installations. These load centers come in various configurations, including single-phase and three-phase, and are suitable for overhead and underground applications.
Rapid Shutdown Device
According to the National Electrical Code (NEC), all solar panel systems must have a rapid shutdown feature that de-energizes the system. The purpose of this requirement is to ensure the safety of firefighters in case of a fire. Even if the inverter is turned off, some solar systems can still leave wires and circuits energized, creating a risk of shock for firefighters working on the roof or in the attic. A rapid shutdown device allows the system to be rapidly disconnected in less than a minute, reducing the electrical voltage and minimizing the risk of shock.
Surge Protective Device
Surge protective devices (SPDs) protect electrical systems from electrical surges and spikes that can be caused by lightning or other sources. They can be installed as standalone devices or as components of electrical equipment. In a photovoltaic system (PV), solar energy is converted into electric current. By incorporating an SPD into the system, potential damage to the installation can be prevented, avoiding high maintenance costs and production interruptions.
Wiring
Wiring is crucial in connecting different solar energy components and facilitating energy transfer from one device to another. PV Wire is frequently used to transmit power from the solar panels to the Inverter(s) for conversion and then directed to another component within the photovoltaic system.
The wires are typically made of either copper or aluminum and come in solid or standard forms with insulation. The cables are designed to carry either DC or AC current depending on the position and connection. They are also color-coded to ensure safety and identification, enabling the system operator or inspector to determine which wire controls a particular current (Positive, Negative, Grounded, etc.).
The wires used in standard solar systems are chosen based on their ability to handle specific voltages and wire gauges, which are determined by the voltage. Charge Controller
Charge controllers are essential in regulating the electrical charge within a solar energy system. They control the amount of electric current added to or withdrawn from the batteries, ensuring stable energy flow from solar panels while preventing overcharging and overvoltage. This helps to prolong the lifespan and optimize the performance of batteries, which is crucial in off-grid or hybrid solar energy systems.
Types of Charge Controller
Charge controllers are available in different sizes and technologies, such as MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) and PWM (Pulse Width Modulation). Solar battery chargers are significant for maintaining battery integrity, as sensitive power storage components require careful and consistent regulation. By employing charge controllers, future maintenance costs and upkeep can be minimized.
Various types of charge controllers are available in the market, including:

Simple 1 and 2-Stage Charge Controllers
These controllers use a relay and shunt resistor to control the voltage in one or two stages. They disconnect the solar panel from the battery if the voltage exceeds the limit to prevent overvoltage.

PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) 3 Stage Charge Controllers
These controllers use pulse-width modulation to regulate the battery's charging. They disconnect the solar panel from the battery when fully charged, preventing overcharging.

MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) Controllers
MPPT controllers act as DC-to-DC converters between the solar panel array and the battery bank. They optimize and regulate the higher DC voltage levels from the solar panel and convert them into lower, optimized, and regulated voltage to charge the battery. These controllers are more efficient, providing 10-30% more power to the battery, with an efficiency rate of 94-98%. However, they are also more expensive.
Battery
Solar batteries are significant for storing excess solar power for later use. They are commonly used in off-grid and hybrid solar electric systems to ensure a constant electricity supply even when there is no sunlight or access to a reliable utility grid. In such scenarios, the battery or battery bank is charged using energy collected from solar panels and regulated by a charge controller and inverter. The stored energy can then be used as needed, providing a reliable power source for the system.
Types of Solar Batteries
Different battery technologies and materials enable power storage capability. The most common solar panel battery types are Flooded, Sealed lead-acid (SLA) batteries, and Lithium Ion solar batteries, each using different fluids and acids to hold energy for an extended period with slow power depletion.
Maintenance requirements and expected lifespans of each battery type will vary based on the technology used and how the system operator charges, stores, and withdraws power from the batteries.
Flooded Lead-Acid Batteries
Flooded lead-acid (FLA) batteries are commonly called “wet cell” batteries because their liquid electrolyte can be accessed by removing the battery caps. During the charging process, the water in the electrolyte solution of flooded batteries evaporates, requiring the regular addition of distilled water to maintain proper levels.
This maintenance demand makes flooded batteries suitable only for those willing and able to perform monthly maintenance checks on their battery bank. Improper maintenance can lead to the failure of FLA batteries, making them especially vulnerable. Therefore, most people need help maintaining these batteries properly or committing to the necessary monthly maintenance schedule.
Due to their stringent maintenance requirements, FLA batteries are not ideal for vacation homes, nor would we recommend them for full-time off-grid residences unless you are willing to do the work. However, for dedicated homesteaders and DIY enthusiasts, FLA batteries can be cost-effective, provided they take excellent care of their battery bank.
Sealed Lead-Acid Batteries
Sealed lead-acid (SLA) batteries are so named because their electrolyte compartment is closed, which prevents leakage and harmful fumes. Unlike flooded lead-acid (FLA) batteries, sealed batteries require minimal maintenance and can be installed without a ventilated battery enclosure. Additionally, they can be mounted in any orientation due to their sealed design.
Two types of sealed lead acid batteries are absorbent glass mats (AGM) and gel batteries. AGM batteries are more affordable and perform better than gel batteries in cold temperatures. They are also capable of higher charge and discharge rates, making them the more cost-effective sealed battery option for most off-grid solar applications.
Gel batteries are an older technology that is more expensive than AGM batteries. They take longer to charge and are less widely available. However, gel batteries perform better in high ambient temperatures, making them suitable for hot climates. Despite this, AGM batteries are usually the more cost-effective option.
Lithium Batteries
The cost of lithium solar batteries is generally about three times that of sealed lead-acid (SLA) batteries. However, their longer lifespan, which is around three times longer, means that the higher initial cost is balanced over the system’s lifetime.
Lithium batteries are ideal for those who require a high-performance battery that lasts a decade or more without replacement. They offer faster discharge and recharge rates, are lightweight, and require no maintenance. Moreover, they are modular, so you can start with a smaller battery bank and expand it as needed. Although the upfront cost of lithium batteries is higher, the total cost of ownership falls in line with that of lead-acid batteries over the system’s lifetime.
Conclusion
When considering installing a solar PV system, it’s crucial to evaluate the components of solar energy system carefully. Choosing the appropriate parts of a solar energy system for your home can be daunting, and there are many factors to consider. However, by carefully assessing your power requirements, storage capacity, and grid connection needs, you can make an informed decision and select the best components for your solar energy system. This way, you can enhance your daily life while reducing your carbon footprint with the right components of a solar energy system.
When determining the best PV system for your home, evaluating your power requirements, storage capacity, and grid connection needs is essential. The system design will depend on the amount of power required for your application, and the number of panels needed will vary accordingly. Therefore, it’s critical to thoroughly examine your options and available suppliers to make the best decision.
Moreover, it’s worth considering the long-term benefits of installing a solar PV system, such as reduced energy bills, increased energy independence, and a potential return on investment. Additionally, by utilizing renewable energy, you’re contributing to a cleaner environment, reducing your carbon footprint, and helping to combat climate change.
While selecting a solar PV system for your home may seem overwhelming, taking the time to research and consider your options thoroughly can pay off in the long run. By making an informed decision, you can improve your daily life and contribute to a sustainable future.
FAQs
A solar panel is a device that converts sunlight into electricity. It comprises photovoltaic cells that absorb sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity.
The price of a 665 watts Canadian Solar Panel in Pakistan, is approximately Rs. 64,000.
The cost of a 5kW solar panel in Pakistan, which includes complete installation, typically varies between Rs. 1,300,000 to Rs. 1,500,000, with occasional fluctuations in price.
The price of a small solar panel in Pakistan can vary depending on the brand, size, and wattage. A small solar panel with a wattage capacity of around 50 watts can range between Rs. 6,000 to Rs. 10,000. However, prices may vary based on market conditions and the purchase location.
As of 2023, the price of a solar panel for a 1-ton AC in Pakistan is around Rs. 94,800.
In Pakistan, the cost of a 5KW solar panel system ranges from Rs. 9,50,000 to Rs. 1,000,000. On average, a 5KW solar panel system generates a daily output of 21 to 25 units.
An inverter is a device that converts DC electricity from solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity that household appliances and electronics can use
The cost of a 5KW solar inverter in Pakistan falls within the price range of Rs. 9,50,000 to Rs. 1,000,000 and typically generates an average daily output of 21 to 25 units.
The lead-acid battery is a popular and reliable choice for solar energy storage in Pakistan due to its affordability and dependability.
A charge controller is a device that regulates the amount of charge going into a battery bank. It prevents overcharging and undercharging of batteries, which can cause damage and reduce lifespan.
Batteries store excess energy produced by the solar panels during the day for use at night or during periods of low sunlight. They are an essential component of off-grid solar energy systems.
A solar tracker is a device that follows the sun’s movement throughout the day to maximize the amount of sunlight that hits the solar panels. It can increase the energy output of a solar energy system by up to 25%.
A grid-tied solar energy system is a system that is connected to the electrical grid. It allows excess energy produced by the solar panels to be sold back to the utility company, reducing or eliminating the need for battery storage.
The lifespan of batteries in a solar energy system depends on the type of battery and how well it is maintained. AGM and gel batteries typically last 5-10 years, while lithium-ion batteries can last up to 20 years.
A solar energy system requires minimal maintenance. The solar panels should be cleaned periodically to remove dirt and debris. The battery bank should be checked regularly to ensure it is adequately charged and not overcharged or undercharged.